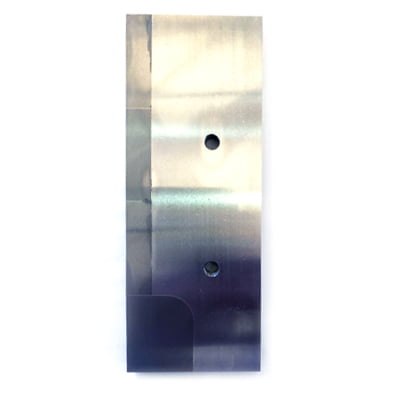
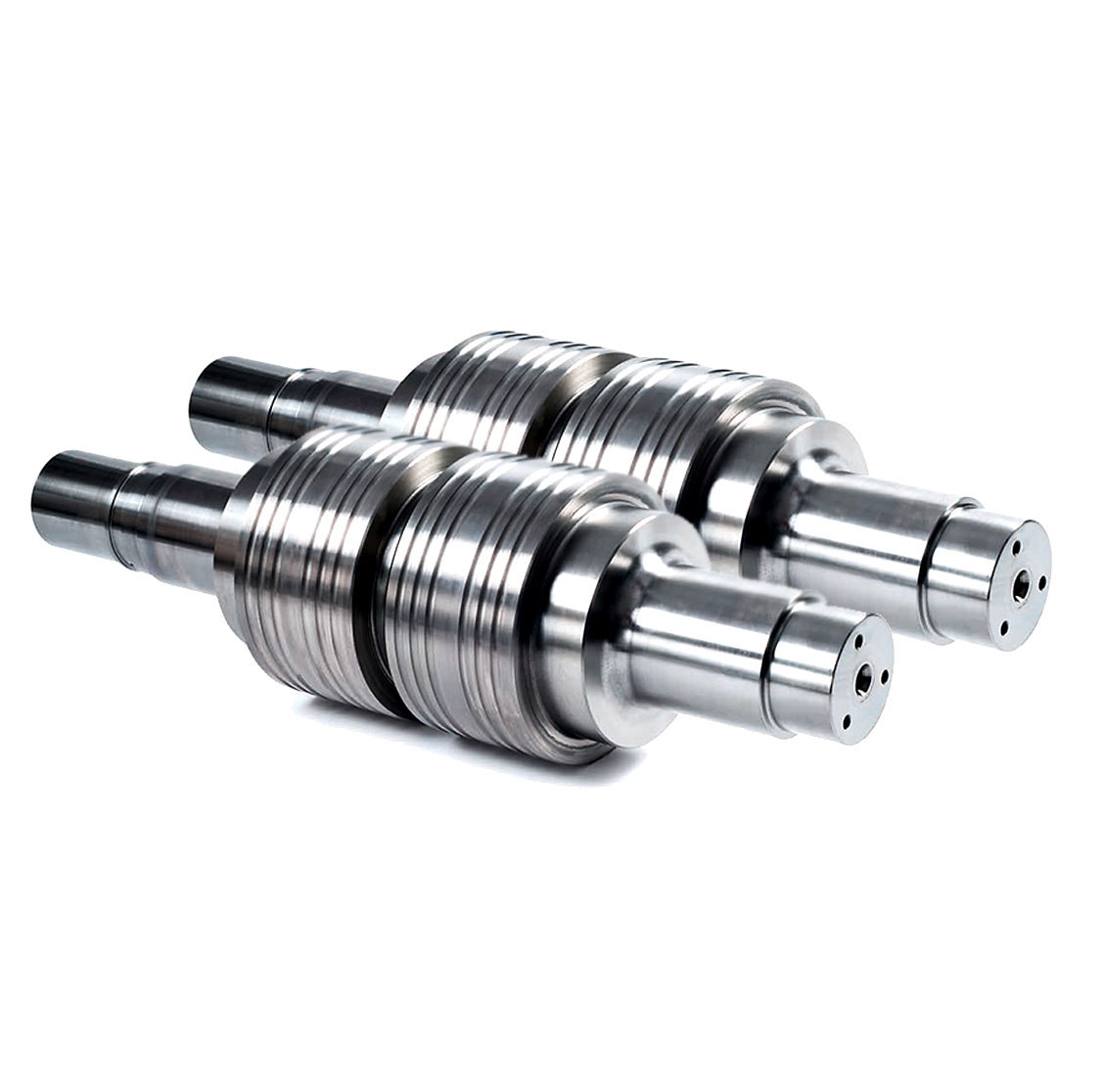
Usually the main working parts of the die are made with Cemented Carbide and we can call it Carbide Die,or Mold, Tooling.
Of course, this is a vague concept, there are many types of molds that are made with Cemented Carbide, and different products require different types of die manufacturing.
Through this article we can quickly understand what are the types of dies and molds that are made using carbide?
Understand the basic characteristics of Cemented Carbide molds, the key matters of Cemented Carbide mold design, what Cemented Carbide grades are used to manufacture molds for different purposes?
The processing methods of Cemented Carbide and so on.
What are carbide stamping and forming dies?
Stamping die is a special kind of process equipment for processing materials (metal or non-metal) into parts (or semi-finished products) in cold stamping process, which is called cold stamping die. Stamping, a method of pressure processing, is the use of a die mounted on a press to apply pressure to a material at room temperature, causing it to separate or plastically deform, so as to obtain the desired part.
High-speed stamping progressive die for motor iron core, IE iron core tungsten carbide
Also known as motor iron core stator stamping die, motor iron core stamping die, silicon steel sheet stamping die.
Motor iron core stamping die refers to the application of motor iron core production and manufacturing molds, is the motor iron core stamping necessary production tools. According to the mold processing accuracy, generally believe that the mold error within 0.02 mm can be called precision mold, the other for the ordinary mold. Carbide silicon steel high-speed stamping die life of 150-200 million strokes or more, carbide edge grinding life of 3 million strokes or more, stamping speed is generally 200 to 400 times/min range of work, according to the needs of the mold can be set up “electronic monitoring technology device”.
Motor core stamping die in accordance with the mold technology category, can be divided into a single process mold, composite mold, progressive die, etc.; according to the number of progressive die columns, can be divided into a single-column progressive die, double-column progressive die, three-column progressive die, multi-column progressive die, etc., mold manufacturing cycle of 3-4 months. Composite or progressive dies will use carbide as punches or inserts.
connector, leadframe carbide high-speed stamping progressive die
The leadframe die is a special die used to produce leadframes, usually made of die steel and carbide. Mold design and manufacturing requirements for precision, to ensure that the manufacturing process can produce accurate, standardized lead frame to meet the design requirements of electronic products.
IC lead frame precision high-speed stamping die for stamping manufacturing accuracy of 2μm, surface roughness Ra0.10μm, die life of 100 million strokes or more, carbide edge grinding a life of 3 million strokes or more, punch speed of 450 times per minute or more!
High-speed progressive die for air-conditioner fin stamping with carbide.
The fin stamping progressive die covers the manufacturing of household air conditioner fins, automobile air conditioner fins, industrial air conditioner fins, large-scale cold storage radiator fins, integral tube-through air conditioner fins and new type of high-efficiency air conditioner fins with shaped holes. The manufacturing precision of the mold is up to 2μm, the surface roughness Ra 0.10μm, the life of the mold is up to more than 500 million punches, the life of one sharpening is up to more than 10 million punches, the speed of punching is up to more than 280 punches/min, and the cycle of the mold manufacturing is 3-4 months. Mold technology function, a mold can be punched 72 columns of products.
Carbide Progressive Die for Electron Gun Parts
Color tube electron gun parts progressive die, for example, manufacturing accuracy of 2μm, mold life of 100 million strokes or more, manufacturing cycle 2-3 months. Mold technology function, can be realized in a pair of molds with the same material different models of products. (In 2023 the market demand for such molds is already small)
Stamping and drawing carbide die for metal cases
Used for manufacturing metal shell stamping molds, such as lithium battery shells, small motor shells, electronic cigarette shells, bullet shells and so on.
This type of mold manufacturing precision of 2μm, mold life of 100 million strokes or more, manufacturing cycle of 3 months. The technical function of the mold, the products are deep-drawn in both directions and punched out 5 pieces in one mold, which reflects the high level of the mold and the high efficiency of the production products.
High-speed stamping carbide progressive dies for hardware stampings
This kind of molds is used for manufacturing common articles in life. Stamping parts are the most commonly used kind of hardware parts, which is a forming processing method to produce plastic deformation or separation of plates, strips, tubes and profiles by applying external force on them through high-speed punches and molds to obtain workpieces of required shapes and sizes, and the workpieces obtained are stamping parts. The dimensional accuracy of these products does not need to be too high, the demand is large, and the carbide progressive die can produce these products very quickly.
Metal button high-speed stamping carbide die
Stamping dies for metal buttons, tungsten carbide molds can be used to produce metal buttons, such as the common metal buttons for jeans, backpack metal buttons, etc., in high speed and high volume.
- Metal zipper high-speed stamping die
Metal zipper is mainly made of alloy copper, stainless steel and other materials. The metal zipper forming equipment is different from our common stamping equipment. The efficiency of metal zipper manufacturing equipment is very high, its running speed can reach 2000 times per minute, so it is very demanding on the molding tool material.
Cemented Carbide Cold Heading Die, Bolt Die, Nut Die, Nail Die
Cold heading mold is the mold that makes blank cut off, preform and form into cold formed parts on cold heading machine. Cold heading molds are subjected to intense stamping loads and high compressive stresses on the surface of the concave mold. The mold material is required to have high strength, toughness and wear resistance. This type of mold is necessary for manufacturing fasteners, which can produce fasteners quickly and in large quantities. At the same time, Cemented Carbide can also be used to make hot heading molds, hot pressing molds, is a kind of molds used to make high-precision parts. It is used to make high precision parts by heating the material to a certain temperature and then applying high pressure to deform the material, thus realizing the manufacture of parts.
Carbide drawing die, wire drawing die, pipe drawing die
Drawing dies are used to manufacture various metal wires, rods and tubes. Cemented carbide wear resistance, corrosion resistance, impact resistance, etc. can be very good to meet the metal material drawing process. With the development of material science and technology, the emergence of CVD coated Cemented Carbide drawing dies makes the drawing dies have a more substantial increase in the life of the mold, the product surface finish is better.
Cemented carbide powder metallurgy die, metal powder pressing molding die, pill pressing molding die
Powder molding die as the name suggests is to make the powder through the mold pressing mold. According to the different powder being pressed, there are metal powder pressing mold, magnetic material powder pressing mold, non-metallic powder pressing mold. Some magnetic material powder metallurgy molds require the use of non-magnetic cemented carbide, and pharmaceutical pressing molds require the use of nickel-based cemented carbide only, as cobalt may pose a health problem (frequent injection of cobalt preparations or exposure to excessive amounts of pristine cobalt can cause cobalt toxicity).
Carbide molds for forming glass aspheric lenses
Used in the manufacture of glass aspheric lenses, these molds use cemented carbide with no bonding phase or very low bonding phase. Because the glass lens in the pressing process needs to be heated to 400-600 ℃, so that the glass softens easier to mold.
Manufacturing these types of molds requires ultra-precision machining equipment to complete, and the surface roughness of the molds is typically 10 nanometers. This is a difficult job for the average mold maker.
Application of Cemented Carbide in Plastic Molds
Cemented Carbide in Plastic Molds can be used to make hot runner nozzles. The nozzles used in injection molds are an important part of the hot runner system mounted on the manifold. The use of Cemented Carbide in plastic molds for parts that are prone to wear and tear can dramatically increase the service life of the mold.
The basic understanding of cemented carbide Die materials
We first understand what is Cemented Carbide?
Cemented carbide is a kind of tungsten carbide powder + cobalt points + other carbide powder, through powder metallurgy pressing sintered composite materials. Tungsten carbide is a kind of high hardness material, through high temperature sintering “glue” metal cobalt (nickel) melting tungsten carbide particles together, forming the tungsten carbide we use. The role of cobalt (nickel) in cemented carbide is similar to that of a “skeleton”. Cobalt content changes the hardness of tungsten carbide will also change, the more cobalt content, the lower the hardness, and vice versa, the lower the cobalt content, the higher the hardness. The finer the particle size of tungsten carbide powder, the higher the hardness, and the coarser the particle size of tungsten carbide powder, the better the impact resistance.
Used as mold tungsten carbide is an excellent material. High hardness, good abrasion resistance, corrosion resistance, impact resistance and other characteristics make Cemented Carbide as mold material is almost a perfect material solution.
Selection of grades of Cemented Carbide for Dies?
Different application scenarios of Cemented Carbide molds use different Cemented Carbide grades (compositions). Here we briefly summarize the different grades (compositions) of Cemented Carbide that are suitable for what kind of Dies.
3.1 Fine-grained cemented carbide grades, such as Yatech’s YU20 tungsten carbide particle size of less than ≤1um, cobalt ≤8%, HRA92-94
Suitable for the manufacture of metal wire drawing, pipe drawing molds, but also suitable for the manufacture of powder metallurgy molds.
3.2 Double crystal grains of cemented carbide grades, such as Yatech’s YF40H tungsten carbide particle size less than 0.4-3.0um, cobalt ≤ 15%, HRA88-90
Suitable for the manufacture of motor cores, silicon steel sheets, metal lead frames and other high-speed stamping progressive mold punches, concave molds, inserts and so on.
3.3 Coarse-grained carbide grades, such as Yatech’s YF55H tungsten carbide particle size less than 0.4-3.0um, cobalt ≤15%, HRA88-90.
Carbide die material selection needs to be considered comprehensively, the hardness of the stamped material, thickness, stamping speed, mold precision, stamping equipment precision and other issues.
What are the machining methods for cemented carbide?
4.1 Electrical discharge machining
Electrical Discharge Machining, wire erosion or spark erosion, is a non-traditional machining process that relies on electrical discharges (or sparks) to remove material particles from workpieces made of conductive materials. The process is particularly well suited for producing complex or fine holes and features in metal parts, as EDM machining is capable of achieving tolerances within +/- 0.005 mm and therefore provides high precision.
Unlike other machining technologies, EDM is characterized as a non-contact process. This means that the tool is never in physical contact with the workpiece. Instead, a series of successive electrical charges are sent from a power source through the tool (called an electrode), which creates an electric arc between the electrode and the workpiece. The sparks generated by this electrical reaction are highly targeted and erode particles on the workpiece in a controlled manner. Being submerged in a dielectric fluid, these particles can be safely flushed away from the electrode and workpiece surfaces.
The non-contact nature of EDM offers many benefits. For one, it eliminates the risk of tool marks and burrs. It also facilitates the machining of small, thin-walled and fragile parts or assemblies that are at risk of damage due to direct contact with conventional machining tools.
EDM is often used in conjunction with other machining or manufacturing processes. For example, in the aerospace industry, metal engine turbines are produced using traditional machining processes and then EDM’d to add fine features such as narrow cooling holes EDM also offers the unique advantage of being able to machine pre-hardened steels and other heat-treated metals without changing their properties or hardness.
Despite its extensive capabilities, the EDM is no more difficult to operate than any other CNC machine.
4.2 Diamond tool cutting and grinding (machining centers)
4.2.1 Electroplated Diamond Cutting Blades
Precision parts processing plant can not be separated from cemented carbide, we often see the cemented carbide processing technology is cutting. Cutting is one of the commonly used ways of undercutting cemented carbide rods, plates and wires. For grooving or cutting below 1mm, diamond ultra-thin cutting blades are commonly used for processing.
Diamond resin matrix type cutting discs, in which the outer ring band is the resin bond abrasive working layer, the center part of the high-strength and high rigidity of the metal material, generally used for medium and large depth of cut grooving and cutting.
In the process of turning carbide parts, the hardness of the tool itself must be higher than the hardness of the workpiece to be processed, so at present, the tool material for turning and processing carbide parts is mainly made of high hardness and high heat-resistant non-metallic binder and diamond.
When cutting carbide parts with hardness less than HRA90, we generally choose BNK30 CBN tools for large margin turning. When cutting carbide parts with hardness greater than HRA90, we generally choose PCD tools made of CDW025 or use resin bond diamond wheels for grinding.
4.2.2 Electroplated diamond grinding head
When processing complex curved shapes, holes and threads, you can use electroplated diamond grinding head of high-speed CNC machining centers for grinding, which has the characteristics of high efficiency and high dimensional accuracy.
4.3.3 Other diamond tools
For the milling process of cemented carbide parts, according to the customer’s demand, we can provide CVD diamond coated milling cutter and diamond inserted milling cutter for precision parts machining, which can replace the electrolytic corrosion and EDM process to improve the production efficiency, and product quality.
4.3 Laser processing
Laser perforation machine is currently the most outstanding of all perforation equipment, laser perforation through the laser generator focused high-density energy on the surface of the workpiece, so that the workpiece is irradiated on the region of local instantaneous melting and gasification, this process lasts a very short period of time, milliseconds within the completion of the process, you can quickly form holes or holes in the groove. Especially applied in
Carbide laser drilling do not have to worry about burrs, it is non-polluting, high-precision processing, processing of the perforated surface is very smooth, without the need for subsequent reworking and polishing, reducing the tedious process. Processing in non-touch processing, the laser head will not be in contact with the material surface, do not have to worry about scratching the workpiece, there is no mold loss, only need a simple package can be very convenient.
Design of carbide die need to pay attention to the key issues
Carbide stamping die, now has come into the actual production of many stamping factories, so what exactly is a carbide die? This kind of die due to the relatively high price, in the design of the time and general mold compared to what need to pay attention to?
Cemented carbide stamping die refers to the use of cemented carbide to manufacture the upper or lower die, or upper die, lower die are made of cemented carbide stamping die. The upper die and lower die can be made of the whole piece of cemented carbide, or a piece of cemented carbide can be glued or set on the steel part as the working part for stamping, and a layer of cemented carbide can also be sprayed on the edge of the steel stamping die. Because of the high hardness and abrasion resistance of cemented carbide, the life of cemented carbide stamping die is several times to dozens of times higher than that of general steel stamping die. Because of the brittle nature of cemented carbide and the impact load in the stamping process, the cemented carbide commonly used in stamping dies are YF40H, YF50H, YF55H and so on.
Characteristics of Cemented Carbide Stamping Die and Problems to be Attentioned in Designing
The upper and lower molds are made of cemented carbide. The structural form of the stamping die is similar to that of general stamping dies, but it also has its characteristics. Now, according to the characteristics of cemented carbide itself, it explains the problems that should be paid attention to when designing the stamping die of cemented carbide.
- Cemented carbide due to more brittle, can not have too much deformation force, all in the design of the material, need to pay attention to the location of the first cutter, can not only punch half a hole, so as to avoid the die bending fracture.
- material belt than the normal stamping design to be larger, and should be greater than the material thickness, so as to avoid the material belt is too small in the stamping was squeezed into the die.
- die clearance in the normal clearance on the basis of the appropriate increase in margin.
- choose a good rigidity of the die frame, stamping molds on the selection of various parts and components to match the high life of the lower die. Such as the upper and lower die holder are made of steel, and to be about 1.5 times thicker than the general stamping die. Positioning nails, guide plate and other accessories made of 45 steel and quenched. The back of the upper and lower molds should be thickened and quenched.
- The guiding accuracy and service life of the die holder should be high in order to be compatible with the high service life of the lower die. Often use rolling guide mold frame and interchangeable guide pillar, large or complex workpiece commonly used 4 guide pillars. Generally, floating die shanks are commonly used to overcome the influence of press error on guiding accuracy.
- The upper and lower mold can be made of the whole piece of tungsten carbide, can also be used in the form of mosaic. Can also be bonded or welded on the steel parts.
- If the unloading plate is used to unload the material, the unloading plate should be prevented from hitting the lower mold of cemented carbide, so that the lower mold is not uniformly loaded and cracks are produced. For this reason, the height of the unloading plate should be higher than the height of the guide plate – the height of the thickness of the material is 0.05-0.01mm lower, then the unloading plate only play a role in unloading the material does not play a role in the pressure of the material. Stamping thin material must be pressed stamping, can be in the unloading plate and the lower die or the upper die between the fixed plate to increase the guide column, guide the unloading plate uniformly pressed workpiece.
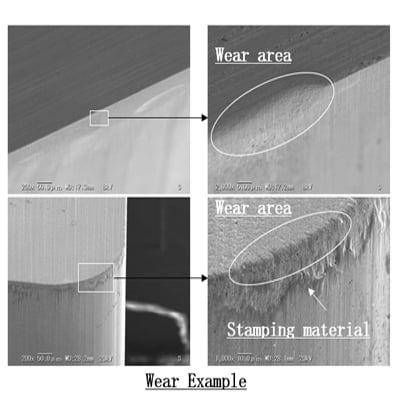
Cemented carbide die use in the process of failure and how to deal with?
6.1Cemented carbide dies may have the following kinds of failures in the course of use:
- wear and tear: the surface material of the die will wear and tear with long time use, and the precision and service life of the die may be affected when the wear and tear is serious.
- fatigue: metal fatigue may occur in long time use of the die, resulting in cracks, deformation and other problems.
- Accumulation: In some specific die use environment, there may be metal materials or other foreign materials accumulated on the surface of the die, affecting the normal use of the die.
6.2For these failures, we can take the following measures to deal with:
- control the use of conditions: in the use of the process, to control the use of conditions of the die, try to reduce the wear and fatigue of the die, to avoid excessive wear and fatigue failure.
- regular maintenance: regular maintenance of the die, including cleaning the surface of the die of accumulated material, repairing die wear and cracks, to extend the service life of the die.
- Use high quality material: choose high quality carbide material when making the die, which can effectively reduce the wear and fatigue of the die and improve the durability of the die.
- Reasonable design of die structure: when designing the die, reasonable structure design can be adopted to reduce stress concentration and wear of the die in the process of use and improve the service life of the die.
In conclusion, for the failure situation of cemented carbide dies, it is necessary to take comprehensive measures to cope with it from the aspects of use condition control, regular maintenance, material selection and structure design, etc., so as to ensure the normal use of the dies and prolong the service life of the dies.
How to repair and maintain cemented carbide dies?
Repair and maintenance of carbide dies requires attention to the following points:
- Cleaning: Clean the die regularly to remove impurities and dirt accumulated on the surface, which can be cleaned with solvents or detergents and then dried thoroughly.
- Lubrication: Lubricate in the appropriate areas to reduce wear and friction and extend the life of the die. Use lubricant or grease for lubrication, but be careful not to use too much lubricant.
- Inspection: Regularly inspect the surface and structure of the die for any damage or wear and tear, detect problems and repair them in time to avoid further deterioration.
- Storage: After using the die, it should be properly stored in a dry and ventilated place to avoid moisture and rust.
- Maintenance: According to the frequency of use and situation, regular maintenance of the die, including cleaning, lubrication and inspection, to ensure that the die is in good working condition.
8.How to deal with carbide die scrapping?
When a carbide die reaches the end-of-life standard, the treatment usually includes the following steps:
- Thorough inspection: first of all, the end-of-life carbide die needs to be thoroughly inspected to confirm whether there are any parts that can be repaired or re-processed for use.
- Disassembly and separation: The die is disassembled and the components are separated, such as the body of the die, replaceable parts, and so on.
- Recycling: For parts that can still be used, they can be processed and repaired, reused or recycled.
- Disposal: For parts that cannot be repaired or reused, they need to be disposed of in a reasonable manner, which may include recycling them into waste materials or other environmentally friendly treatments to ensure minimal impact on the environment.
- Documentation and analysis: The disposal of end-of-life dies is documented and analyzed for future improvements in design and production processes to reduce the likelihood of die obsolescence.