What is Tungsten Carbide that Corrosion Resistant
Corrosion Resistant Carbide,Corrosion-resistant WC (tungsten carbide), Rust-resistant tungsten carbide, Tungsten carbide for corrosion prevention, Corrosion-proof carbide, Anti-rust tungsten carbide
1. Classification of metal corrosion
Classification according to corrosion mechanism Metal corrosion can be classified into chemical corrosion, electrochemical corrosion and physical corrosion according to the corrosion mechanism, among which electrochemical corrosion is the most common and the most serious harm to the metal.
1.1 Chemical corrosion
Chemical corrosion refers to the corrosion caused by the direct chemical reaction between the metal surface and the non-electrolyte.
There is no current generation during the reaction, such as when the cemented carbide is heated in air, the binder cobalt reacts chemically with oxygen in the air to generate loose cobalt oxides;
The characteristic of this type of corrosion is that under certain conditions, the oxidant in the non-electrolyte directly interacts with the atoms on the surface of the metal to form corrosion products, and the transfer of electrons during the corrosion process is carried out directly between the metal and the oxidant, so there is no current generation.
Metal oxidation at high temperature is generally considered to be chemical oxidation, but because high temperatures can cause the formation of semiconductor oxide skin on the surface of the metal, so there are scholars will also be high temperature oxidation into the electrochemical mechanism.
1.2 Electrochemical corrosion
Metal in aqueous solution, and ion-conducting electrolyte electrochemical reaction produced by the damage.
In the reaction process there is current generation, corrosion of the metal surface there is a cathode and anode, the anodic reaction so that the metal loses electrons into positively charged ions into the medium, known as the anodic oxidation process. The cathodic reaction is the oxidant in the medium absorbs the electrons from the anode, known as the cathodic reduction reaction, these two reactions are independent of each other but at the same time, known as a pair of conjugate reaction.
This makes the metal surface cathode and anode form a short-circuit battery, the corrosion process has current generation, such as metal in the atmosphere, seawater, soil, acid and alkali salt solutions, tap water, water for injection and other media corrosion belongs to this category.
1.3 Physical corrosion
refers to the metal and the surrounding medium occurs purely physical dissolution and the resulting damage. Metal in the liquid metal high temperature molten salt, molten alkali can occur in the physical dissolution.
Physical corrosion is caused by the migration of substances, solid metal in the liquid medium dissolved and transferred to the liquid, making the metal damage, so there is no current generation, is a purely physical process.
2. Characteristics of corrosion resistant tungsten carbide
The design of tungsten carbide grades needs to be based on different types of corrosion for the composition ratio design study.
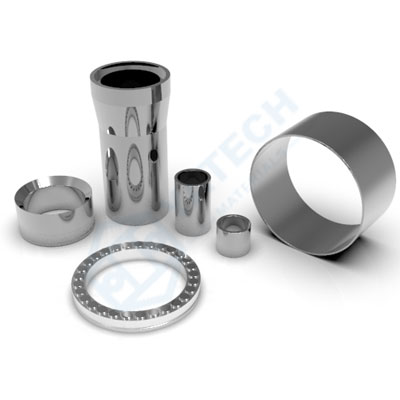
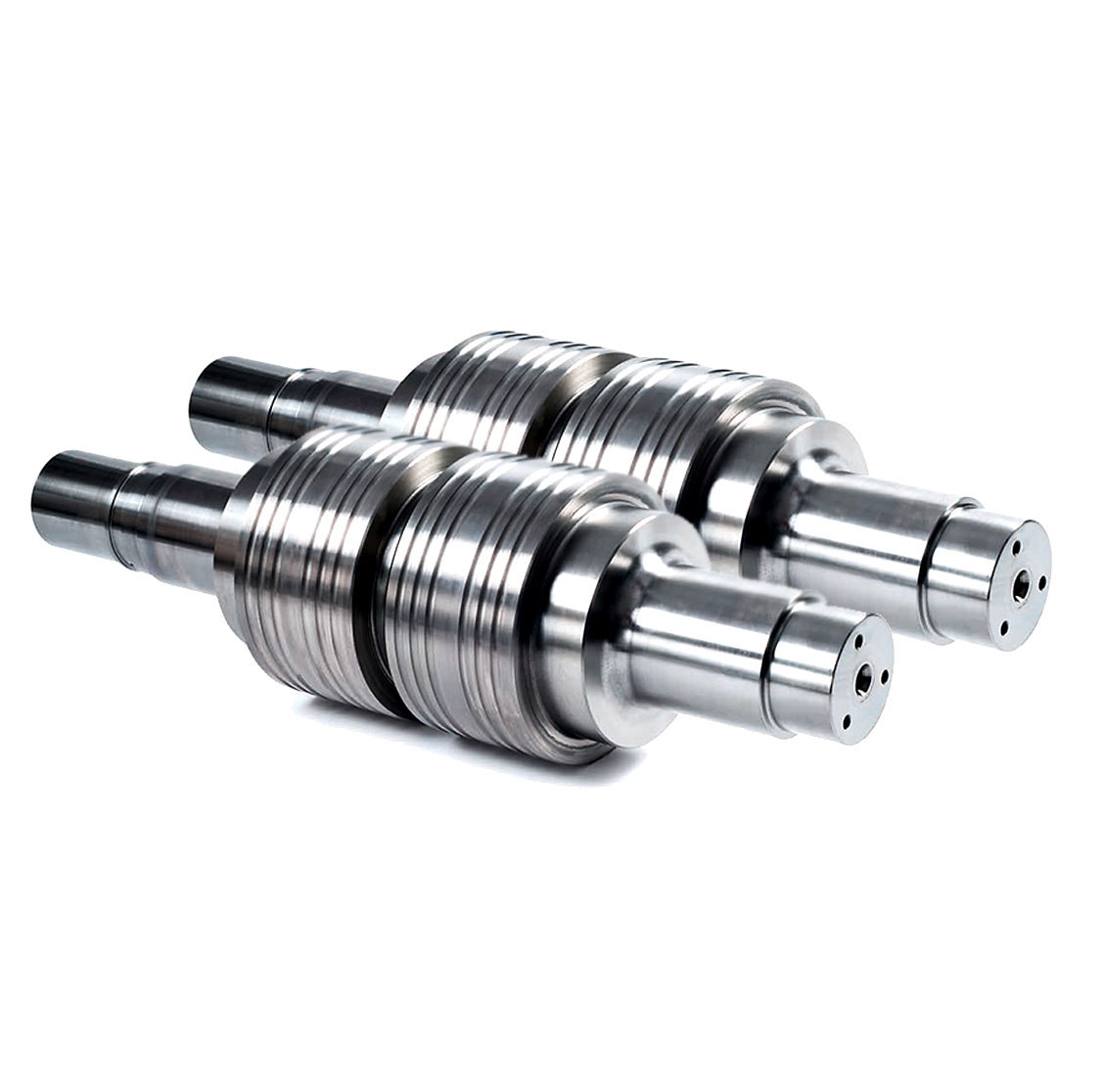
Corrosion-resistant tungsten carbide used in the oil and gas industry extraction and transport equipment, the main corrosion for chemical corrosion and physical corrosion is usually used WC + Ni + (other carbides) composition. This design of tungsten carbide grades has very good chemical and physical corrosion properties.
Precision stamping die industry uses corrosion-resistant tungsten carbide block, the main corrosion electrochemical corrosion, usually using WC + cobalt + (chromium, nickel, tantalum, niobium and other carbides). This composition ratio design of tungsten carbide grades has very good electrochemical corrosion performance.
3. Applications of corrosion resistant tungsten carbide
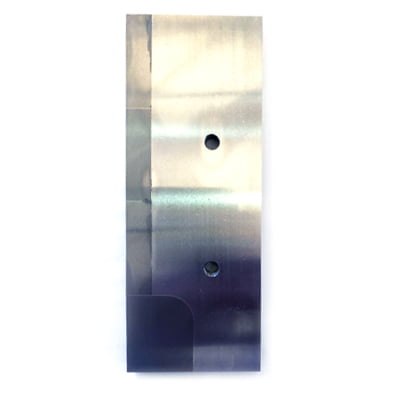
Precision stamping mould punches, inserts, nozzles for oil and gas extraction and transmission equipment, bushings, valve seats… Metal parts that require wear and corrosion resistance, such as crushing blades for food processing equipment, pistons for beverage filling equipment, and sealing parts.
#Benefits of corrosion-resistant tungsten carbide
#How to choose the right corrosion-resistant materials for your industry
#Tungsten carbide vs. other corrosion-resistant materials
#Corrosion-resistant tungsten carbide applications in [specific industry]
#The science behind corrosion-resistant tungsten carbide