Common classifications and uses of cemented carbide
Cemented carbide, also known as metal hard compound alloy material, is an alloy material made of hard compound of refractory metal and bonding metal through powder metallurgy process. There are many kinds of cemented carbide, which are suitable for various cutting, wear-resistant, impact-resistant and other working conditions, so they are widely used in daily production. Next, let’s take a look at the introduction of different types of cemented carbide.
Tungsten carbide has a series of excellent properties such as high hardness, wear resistance, good strength and toughness, heat resistance and corrosion resistance, especially its high hardness and wear resistance, which basically maintains even at a temperature of 500 ° C. Unchanged, there is still a high hardness at 1000 ° C. There are mainly three types of cemented carbide for cutting tools, cemented carbide for geological mining tools and cemented carbide for wear-resistant parts.
1. Cemented carbide for cutting tools
Cemented carbides for cutting tools are divided into six categories: P, M, K, N, S, and H according to the different fields of use;
Class P
Alloys/coating alloys based on TiC and WC, with Co (Ni+Mo, Ni+Co) as binders, are often used in the processing of long-chipping materials, such as steel, cast steel, long-cut malleable cast iron, etc.; Taking the grade P10 as an example, the suitable processing conditions are turning, profiling, threading and milling under the conditions of high cutting speed, medium and small chip sections;
Class M
Alloy/coating alloy based on WC, with Co as binder and adding a small amount of TiC, commonly used in the processing of stainless steel, cast steel, manganese steel, malleable cast iron, alloy steel, alloy cast iron, etc. Fine turning and fine boring under high cutting speed, small load and no vibration.
Class K
Based on WC, with Co as the binder and adding a small amount of TaC and NbC alloys/coating alloys, it is often used in the processing of short chip materials, such as cast iron, chilled cast iron, short chip malleable cast iron, gray cast iron, etc.;
Class N
Alloy/coating alloy based on WC, with Co as binder and adding a small amount of TaC, NbC or CrC, commonly used in the processing of non-ferrous metals and non-metallic materials, such as aluminum, magnesium, plastic, wood, etc.;
Class S
Alloy/coating alloy based on WC, with Co as binder and adding a small amount of TaC, NbC or TiC, generally used for the processing of heat-resistant and high-quality alloy materials, such as heat-resistant steel, nickel, cobalt and titanium alloys. Processing of various alloy materials;
Class H
Alloy/coating alloy based on WC, with Co as binder, adding a small amount of TaC, NbC or TiC, commonly used in the processing of hard cutting gifts, such as hardened steel, chilled cast iron and other materials;
2. Cemented carbide for geological and mining tools
According to the different parts of use, it is divided into the following categories
1) Cemented carbide for rock drilling bits; operating conditions such as grade YA05, suitable for soft rock or medium hard rock with uniaxial compressive strength less than 60MPa, grade YA50/YA60 suitable for uniaxial compressive strength greater than 60MPa 200MPa hard rock or extremely hard rock; as the number of grades increases, the wear resistance decreases and the toughness increases.
2) Cemented carbide for geological exploration;
3) Cemented carbide for coal mining;
4) Cemented carbide for mining and oil field drill bits;
5) Cemented carbide for composite sheet matrix;
6) Carbide for snow shovel;
7) Carbide for excavating teeth;
8)Extruder screws, augers, mixer paddles, linings, sleeves
Perforated and multi-hole plates, screw segments, shaping rolls, slippers, dies;
The Rockwell hardness of this type of alloy can reach HRA85 and above, and the bending strength is generally above 1800MPa.
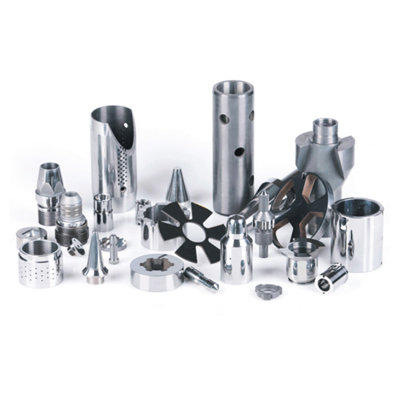
3. Cemented carbide for wear-resistant parts
According to the field of use, it is divided into:
1) Cemented carbides for drawing metal wires, rods, tubes and metal shells, such as lithium battery shell drawing dies, steel cord drawing dies, cold heading of fasteners, etc., metal forming tools.
2) Cemented carbide for stamping dies, such as silicon steel sheet, electronic connector stamping, fastener stamping, steel ball stamping dies, etc.
3) Cemented carbides for high temperature and high pressure components, such as top hammers and cylinders for synthetic diamonds.
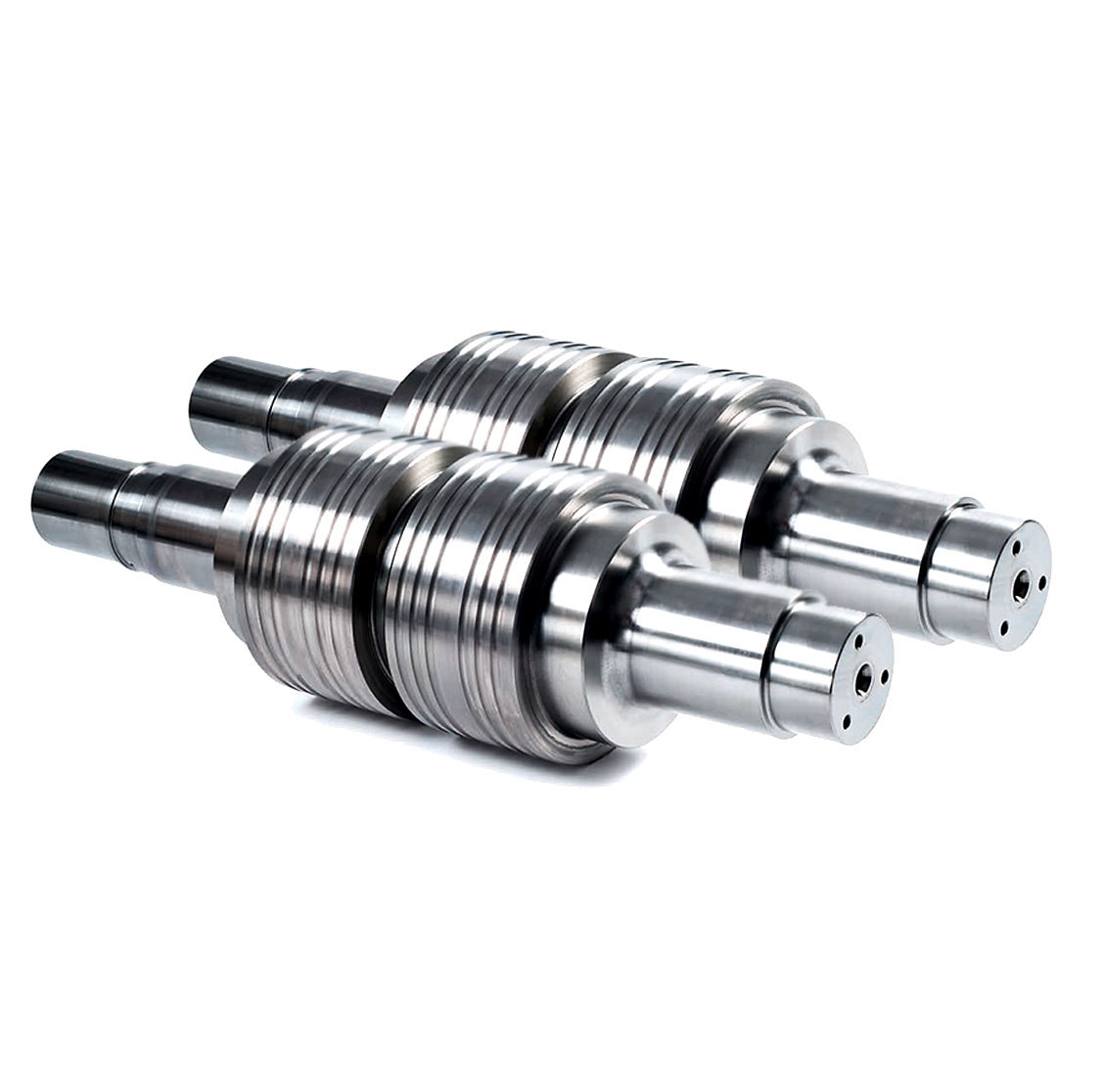
4) Cemented carbides for wire rod rolling rings, such as roll rings for high-speed wire rod rolling finishing mills, etc.
Carbide can be used in other areas that require wear resistance.