Carbide use process will have some questions, we through years of industry cases, to provide you with answers.
1.Tiny cracks appear after machining of Cemented Carbide
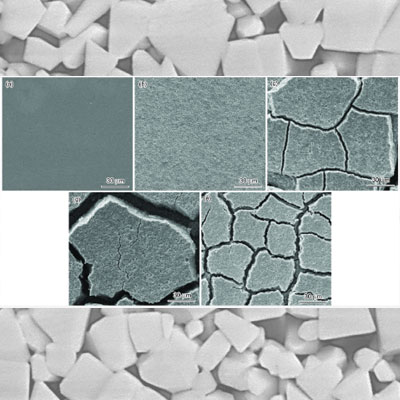
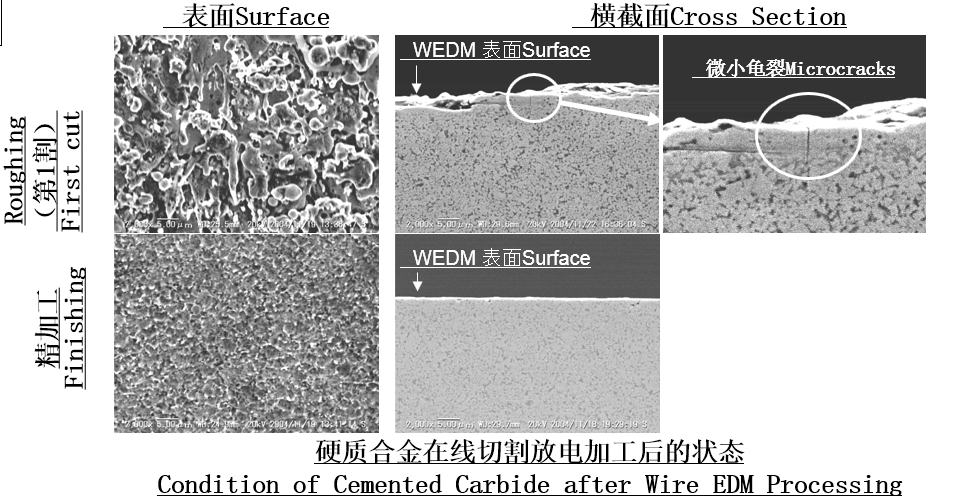
There is a possibility of micro-cracking during wire-cutting or spark machine discharge machining of Cemented Carbide. Tiny cracks are more likely to occur in micro-particle or ultra-micro-particle alloys. It may result in localized cracking of the machined workpiece or finished workpiece.
Cause:
Condensation produced by rapid quenching and cooling after high temperature dissolution of carbide in wire EDM.
Solution and Suggestion:
Reduce the current load during WEDM (increase the wire cutting time).
Elimination of micro-cracks: It is recommended to use a grinding machine for finishing.
Chipping and spalling may occur when processing materials with metamorphic layers and micro-cracks due to the load in the grinding process.
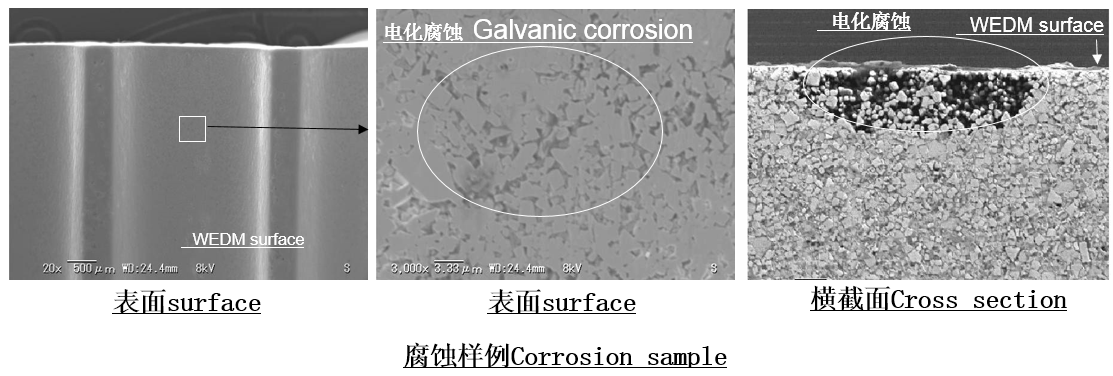
2.Tungsten carbide corroded
Due to the use of water in electrical discharge machining, galvanic corrosion may occur on the surface of cemented carbide. When the cobalt content is higher, galvanic corrosion is more likely to occur. Also, corrosion may occur during storage.
Cause:
In electrical discharge machining using water, current contact can cause galvanic corrosion, as can exposure to moisture.
Solution and Recommendation:
Increase the resistivity of machining water.
Use corrosion resistant carbide (Yatech Materials YA or YF series carbide).
Store in a dry environment.
Use rust-resistant oil.
*Corrosion will not occur during EDM with oil.
3.Cracks in wire EDM of Cemented Carbide
Cracks can occur in carbide during wire-cut electrical discharge machining.
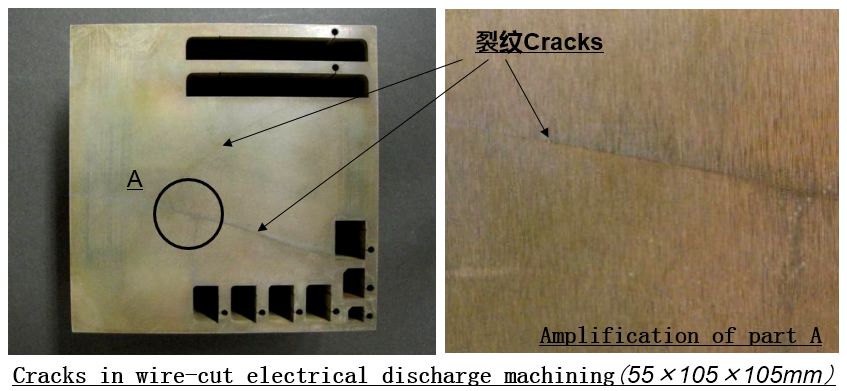
Cause:
A variety of factors cause wire EDM cracking, including high heat and internal stresses during the EDM process.
Thermal shock, tiny cracks, metamorphic layers, galvanic corrosion, etc.
Solutions and Recommendations
Sharpen the upper and lower surfaces of the carbide before wire-cut EDM (basic element).
Cut from the outside to the inside of the carbide, do not cut holes in the center.
Use thinner materi
4.Tungsten carbide spalling
Tungsten carbide has high strength and is resistant to wear. However, when machining loads are high, flaking of tungsten carbide may occur, causing the edge to dull.
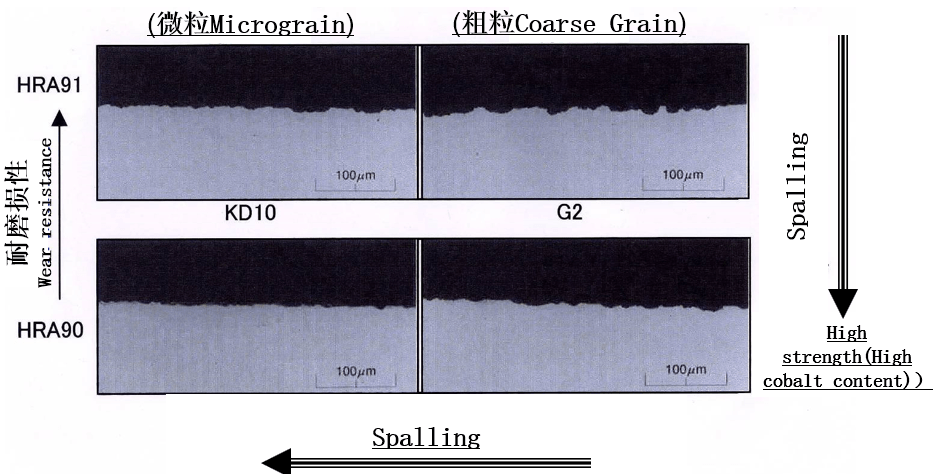
Reason:
Too much machining load in grinding process.
Coarse particles of tungsten carbide (WC).
Solution and suggestion:
Reduce the grinding load.
Select micro-particle alloys and alloys with high cobalt content.
5.Carbide chipped edges and corners
Because Cemented Carbide is hard and fragile, chipping can sometimes occur.
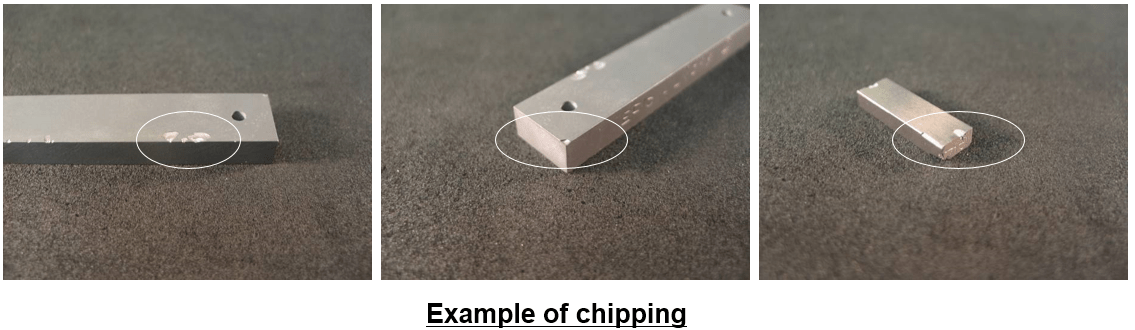
Reason:
Impact during handling and processing
The dimensional accuracy of the part is too low, and there are multi-directional forces.
Solutions and Recommendations
Do not hit the part and do not use excessive impact force during processing.
Improve the dimensional accuracy of the product.
Grinding.
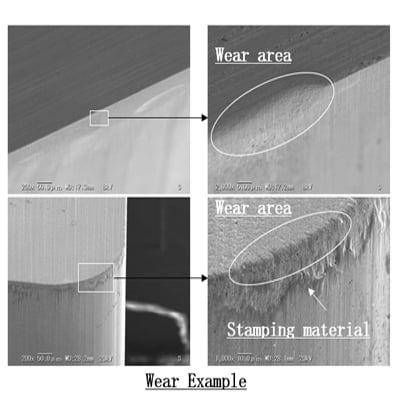
6.Cemented Carbide Wear
Cemented Carbide wear changes from application to application. As the density of the carbide increases, wear decreases. However, high density alloys are prone to spalling. In addition, wear changes depending on the type of material being stamped.
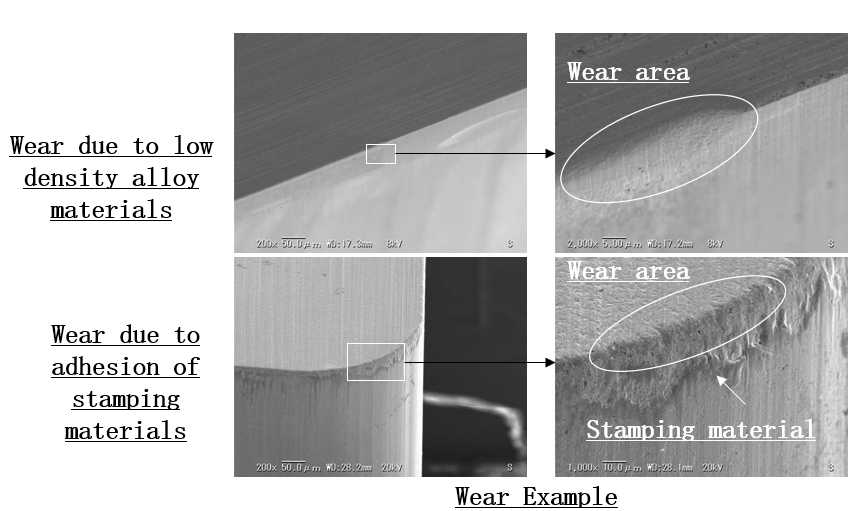
Cause
Low-density alloy material or adhesion of stamping material on the workpiece.
Solutions and Recommendations
Increase the density of the workpiece material.
Use workpiece with anti-adhesion material. Recommendation: YA10, an alloy with low cobalt content.